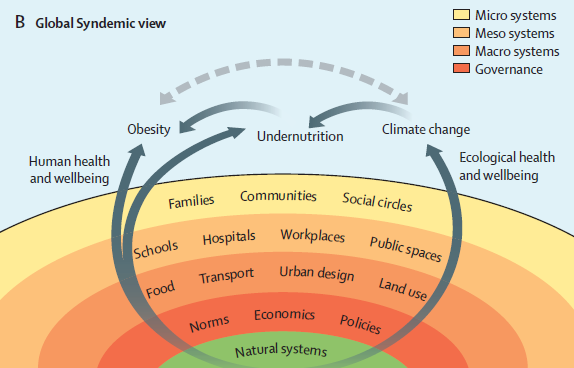
The global increase in obesity is a visible marker of serious systemic problems with contemporary food systems, living environments, and social equity. As co-chair of the Lancet Commission on Obesity (“the Commission”)—an international project led by 43 experts from 14 countries and 22 disciplines that aims to stimulate progress and strengthen accountability systems for the implementation of recommended policies and actions on obesity—I am pleased to share with you the Commission’s seminal report, The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition and Climate Change. Three years in the making, this report is the first to definitively place and critically examine obesity in a wider context of the global interactions of the pandemics of obesity, undernutrition, and climate change. Because these three pandemics are driven by the food, land use, transport, and urban design systems, they may also share common solutions. The links between the pandemics of obesity, undernutrition and climate change constitute The Global Syndemic – they interact in time and place, adversely affect each other, and have common social, economic, or environmental determinants.
Malnutrition in all its forms, including undernutrition and obesity, is the single greatest cause of ill-health and premature death globally, and its already devastating impact on global health is expected to be further exacerbated by climate change. Climate change will increase undernutrition through increased food insecurity from extreme weather events, such as droughts, and changes in the nutrient content of foods. Likewise, fetal and infant undernutrition increase the risk of adult obesity. Climate change may also affect prices of basic food commodities, especially fruit and vegetables, potentially increasing consumption of energy-dense, nutrient-poor processed foods that contribute to obesity. Food production accounts for almost 30% of all greenhouse gas emissions, half of which come from cattle, and beef consumption contributes to colon cancer, cardiovascular disease and obesity.
Critically, the Global Syndemic’s common drivers and interacting outcomes suggest double or triple duty actions that address common solutions. For example, guidelines for a sustainable diet, the restriction of commercial influences, the right to well-being legislation, and policies for healthy, equitable, environmentally-sustainable, economically-prosperous food systems would all have an impact across obesity, undernutrition, and climate change (i.e. triple-duty solutions). Additional actions recommended by the Commission include:
- establishment of a Framework Convention on Food Systems (FCFS) to restrict the influence of the food industry in policymaking and mobilize national action for sustainable food systems;
- redesign of economic incentives, including redirection of $5 trillion in global government subsidies from fossil fuels and large agricultural businesses to sustainable, healthy, environmentally friendly activities; and
- establishment of a $1 billion global philanthropic fund to support civil society in advocating for change.
Decades of research have greatly informed our knowledge of the global obesity pandemic and what can be done to address it, yet implementation of science-based recommendations remains piecemeal and unacceptably slow. This policy inertia reflects powerful opposition by vested commercial interests, lack of political will, and insufficient demand for change by the public and civil society. Like the obesity pandemic, the Global Syndemic is neither an inevitable nor intractable problem—it is the result of manmade systems. Grassroots mobilization may already be underway. For example, sales of sustainably produced foods are growing at 5% per year. Sales of “healthy-for-you” food products are growing more rapidly than traditional lines. Business models that balance health, environmental protection with profit may be those businesses that are likely to succeed long term. Our urgent hope is that joining these three pandemics will offer novel solutions. Our health and the health of the planet are at stake.