Download: Fast Facts - Adolescent Obesity (PDF)
OBESITY is a complex chronic disease in which abnormal or excessive accumulation of body fat impairs health. Adult obesity rates have more than doubled since the 1980s — in the U.S. today, obesity affects over 42% of adults and 18% of youth.1,2 Obesity and its related complications are major drivers of rising healthcare costs, diminished health-related quality of life, and the recent decline in U.S. life expectancy. This fact sheet is part of a series designed to provide basic information about the science of obesity and current strategies to address it.
Key Takeaways
-
Adolescent obesity has risen over the past few decades, putting adolescents at risk of serious complications.
-
Adolescents deserve access to a wide range of safe and effective obesity treatments.
-
Weight stigma can occur across a variety of settings and can be profoundly harmful to adolescents’ health and academic success.
The Prevalence of Adolescent Obesity
The U.S. obesity rate among adolescents aged 12 to 19 years old has risen to 20%, compared to 11% in 1988-1994.2 Disparities exist based on race and geographic location.
- Among American high school students, 2019 obesity rates were:3
- 21.3% for Native American students
- 21.1% for Black students
- 19.2% for Latinx students
- 15.6% for multiple-race students
- 13.1% for white students
- 6.5% for Asian students
- Colorado had the lowest obesity rate for high school students at 10.3%, while Mississippi had the highest at 23.4%.3
Adolescent Obesity Comorbidities
Adolescents with higher BMIs and more comorbidities are more likely to experience a decreased health-related quality of life.4
- Common comorbidities for obesity in adolescents include:5
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Osteoarthritis and joint pain
- Sleep apnea and breathing problems
- Adolescents with obesity may also experience psychological effects. These may include:6,7
- Low self-esteem
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Eating disorders
- Suicidal ideation3
Treating Adolescent Obesity
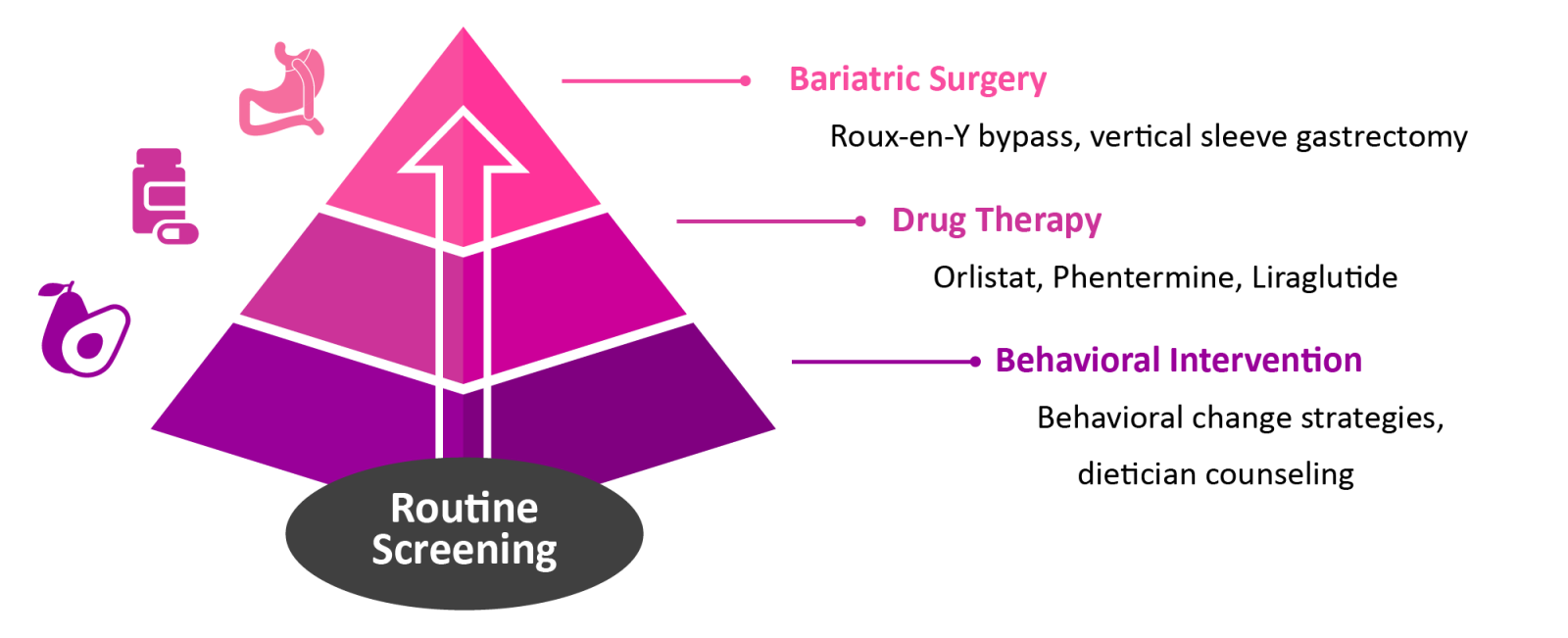
Many of the obesity treatments available to adults are also available to adolescents. However, only three medications have FDA approval for use in adolescents: Orlistat and Liraglutide for patients aged 12 and older and Phentermine for patients over the age of 16. 8,9 Over half of adolescents seeking surgical interventions for obesity were initially denied insurance coverage for the procedure because they were under the age of eighteen.10
Adolescent Obesity and Weight Stigma
Adolescents with obesity can be particularly vulnerable to experiences of weight stigma. Weight stigma can be described as “the societal devaluation of a person because he or she has overweight or obesity” and it is often based on inaccurate and harmful stereotypes.11 Stigmatizing experiences may occur at school, home, a doctor’s office or as a result of the media. Weight stigma is dangerous and may actually worsen obesity for those who experience it.11
- Adolescents who experience persistent weight stigma may be at higher risk for:11
- Emotional and psychological effects such as poor body image, mental illness, substance use or self-harm
- Academic outcomes such as social isolation, victimization, poor grades or skipping school
- Disordered eating behaviors like binge-eating or emotional eating
- Decreased exercise and physical activity behaviors
- References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief, no 360. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2020.
- Fryar CD, Carroll MD, Afful J. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and severe obesity among children and adolescents aged 2–19 years: United States, 1963–1965 through 2017–2018. NCHS Health E-Stats. 2020.
- RWJF. Obesity Rates among High School Students. The State of Childhood Obesity. https://stateofchildhoodobesity.org/high-school-obesity/. Accessed October 6, 2020.
- Nadeau K, Kolotkin RL, Boex R, et al. Health-Related Quality of Life in Adolescents With Comorbidities Related to Obesity. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2011;49(1):90-92. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.10.005.
- University of Rochester Medical Center. Obesity in Teens. Health Encyclopedia. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=…. Accessed October 6, 2020.
- Rankin J, Matthews L, Cobley S, et al. Psychological consequences of childhood obesity: psychiatric comorbidity and prevention. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2016;7:125-146. Published 2016 Nov 14. doi:10.2147/AHMT.S101631
- Zeller MH, Reiter-Purtill J, Jenkins TM, Ratcliff MB. Adolescent suicidal behavior across the excess weight status spectrum. Obesity. 2013;21(5):1039-1045. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.20084.
-
Srivastava G, Fox CK, Kelly AS, et al. Clinical considerations regarding the use of obesity pharmacotherapy in adolescents with obesity. Obesity. 2019;27(2):190-204
-
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. FDA approves weight management drug. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-weight-management-drug-patients-aged-12-and-older. Published December 4, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2021.
-
Inge TH, Boyce TW, Lee M, et al. Access to care for adolescents seeking weight loss surgery. Obesity. 2014;22(12):2593-2597.
-
Pont SJ, Puhl R, Cook SR, Slusser W, , ,. Stigma Experienced by Children and Adolescents With Obesity. Pediatrics. 2017;140(6):e20173034. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-3034.
A product of the Strategies to Overcome & Prevent (STOP) Obesity Alliance at the Sumner M. Redstone Global Center for Prevention & Wellness.